The global value of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) will grow dramatically from $100 million today to $213 billion by 2030, once the virtual money gains greater adoption for domestic payments, according to new data from Juniper Research.
By 2030, 92% of the total value transacted through CBDCs around the world will be paid domestically, as cross-border payment systems face an uphill battle for adoption, Juniper predicted.
The digital currency, which is backed by traditional fiat cash such as the US dollar or British pound, can bolster financial inclusion because customers don’t have to have a bank account to hold them; they can instead use encrypted “digital wallets” that exist in the cloud, on a desktop or laptop, or even on USB storage device.
 Vectorios2016 / Getty Images
Vectorios2016 / Getty ImagesWith a cross-border CBDC payment system, immigrants, for example, could send money back to their countries of origin without having to pay what can be exorbitant fees for electronic money transfers. Businesses would also be able to make cross-border payments for goods and services with much cheaper, and faster, settlements.
Central-bank-backed digital currencies would also reduce the costs of printing and replacing mone, help improve fraud detection, and allow money paid to scammers to be more easily traced and recovered, according to Lou Steinberg, former Ameritrade CTO and managing partner at cybersecurity research firm CTM Insights.
“It would simplify and speed up cross-border payments and reduce the cost and complexity of processing checks, wires, etc.,” Steinberg said in an email reply to Computerworld. “Unlike cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin, a currency that is backed by the full faith and credit of the United States or other trusted government would provide certainty that the value of the currency is being carefully managed. A government can adjust everything from the money supply to interest rates as they manage and maintain the value of a fiat currency.”
Digital currencies also eliminate the anonymous nature of consumer cash transactions. In places such as China, where spending activity is closely monitored, that would let the government know what movies an individual is buying tickets for of whether they are spending money at a bar. Those are hard to track with cash.
The US has been a slow follower compared to other nations, such as China and its digital Yuan, in developing a CBDC. Australia, China, Thailand, Brazil, India, South Korea and Russia already have pilots or will begin test programs this year. By 2030, the Bank of England and UK Treasury are planning to launch a digital pound or ‘Britcoin’ CBDC.
It matters which nation’s digital currency achieves widespread adoption first because that government will be able to set the global rules for most others, according to Steinberg. “Whomever sets up large international payment systems first will have a de-facto standard, one which latecomers will have to adopt,” he said. “The US continues to study a digital dollar while others are making progress. We need to prioritize a system for international payments and settlement based on a digital dollar, almost the equivalent of a next-generation SWIFT network.”
The features and standards can be used to design in privacy or state surveillance and traceability. They can include limited use currency, such as a type of dollar that could only be used for stimulus but not saved, or a digital dollar food stamp.
“On the other hand, countries like Cuba have two types of currency, and limit the use of one type to foreigners only (so they know which of their citizens are collecting money from foreigners),” Steinberg said. “If we want western standards around privacy, we need to set the standards. If we want the dollar to maintain its role as a ‘reserve currency,’ we need to set the standards around cross-border networks. Showing up late to the game means you play by some else’s rules.”
All together, 114 countries representing 95% of global GDP are investigating the creation of CBDCs, according to the Atlantic Council, a Washington-based think tank. Only 10% have launched general CBDC networks. Sixteen percent of projects are in pilot stage, 30% are in development, and 27% are still in the research stage, according to the Atlantic Council.
“We are behind. The good news is that we are starting to realize this,” Steinberg said of the US.
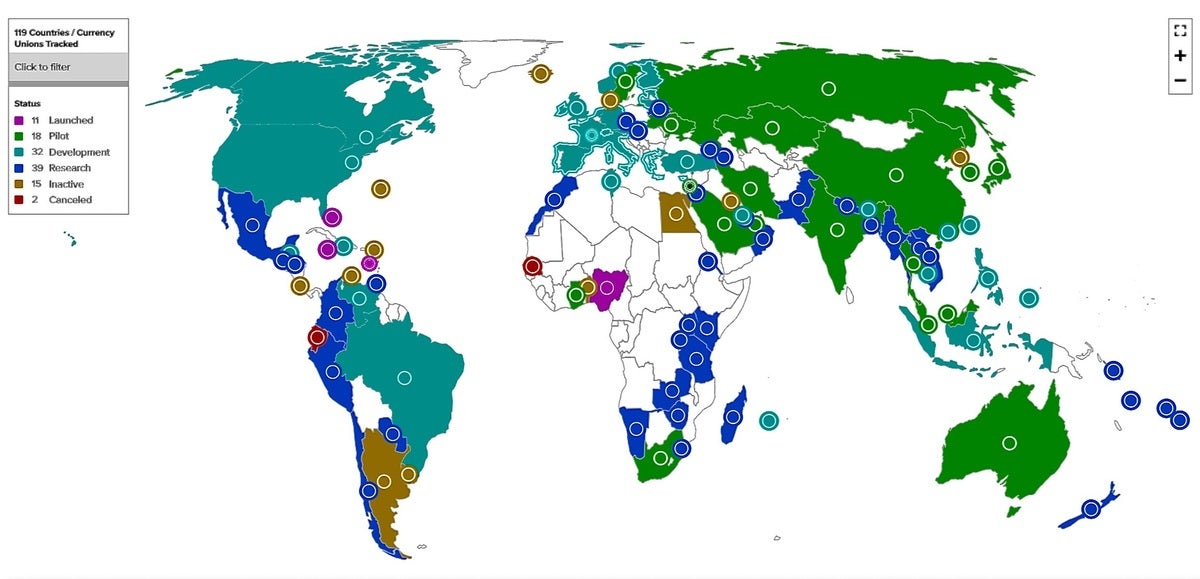 The Atlantic Council
The Atlantic CouncilThis map by the Atlantic Council shows the maturity of CBDC projects around the globe.
In March 2022, for example, US President Joe Biden issued an executive order calling for more research on developing a national digital currency through the Federal Reserve Bank, or “The Fed.” The order highlighted the need for more regulatory oversight of cryptocurrencies, which have been used for nefarious activities such as money laundering. The Fed has been investigating the creation of a CBDC for years.
US lawmakers have also introduced bills that would allow the US Treasury to create a digital dollar. The electronic dollar would allow people to make payments using tokens on mobile phones or through cards instead of cash.
In November, the New York Federal Reserve Bank began developing a wholesale CDBC prototype. Named Project Cedar, the CBDC program hammered out a blockchain-based framework expected to become a pilot in a multi-national payments or settlement system. The project, now in phase 2, is a joint experiment with the Monetary Authority of Singapore to explore issues around the interoperability of the distributed ledger.
Since CBDCs are issued by central banks, they will be mainly targeted at domestic payments at first, with cross-border payments arriving as systems become established and links made between CBDCs used by individual countries. Crucial to CBDC success, however, will be cross-border and retail merchant acceptance.
CBDCs will also require a complex regulatory framework including privacy, consumer protection, and anti-money laundering standards, which need to be made more robust before adopting the technology, according to the Atlantic Council. Any new system of payment could also jeopardize the national security objectives of the country using them.
“They can, for example, limit the United States’ ability to track cross-border flows and enforce sanctions,” the group said. “In the long term, the absence of US leadership and standards setting can have geopolitical consequences, especially if China and other countries maintain their first-mover advantage in the development of CBDCs.”
Steinberg agreed, saying a fully distributed system has risks, “both that wallets will be electronically pick-pocketed, and that transaction validity (consensus) can be cheated. A well-designed system could be quite secure today and future proofed. A poorly designed one would lead to widespread theft and fraud,” he said.
The research by Juniper said to date there is still lack of commercial product development around CBDCs, with few well-defined platforms for central banks to leverage — a big limiting factor for the current market.
“While cross-border payments currently have high costs and slow transaction speeds, this area is not the focus of CBDC development,” said Nick Maynard, Juniper’s head of research. “As CBDC adoption will be very country specific, it will be incumbent on cross-border payment networks to link schemes together, allowing the wider payments industry to benefit from CBDCs.”
For success, any CBDC platform would need a full end-to-end financial network, including wholesale capabilities, digital wallet, and merchant acceptance, Juniper said.
One of the challenges for central banks is figuring out how to enable a CBDC that adds value above existing payment systems, according to Gartner Research. The success of CBDCs also depends on “programmability” enabled by smart contracts, Gartner argued in a January report.
“In order to further justify investments into CBDCs, developers are experimenting with injecting programmability into CBDC-enabled payment value chains,” Gartner said. “Therefore, bank CIOs need to prepare for this transformation,”
As part of ongoing pilots of the digital Yuan, or e-CNY, for example, the Bank of China Chengdu is using smart contracts to manage the deposits for extracurricular school activities, such as field trips to museums. Using the e-CNY CBDC reduces reliance on third parties to deal with a refund if a class is canceled, or a student couldn’t attend, Gartner said.
Countries such as Russia and China see how payments that depend on US infrastructure and currencies can be affected by sanctions and are working to develop alternatives, Steinberg said.
“The one to watch is China,” Steinberg said, referring to the mBridge Project. “Domestically, they need to keep electronic payments from all moving to tech companies, and undoubtedly see benefits in increased consumer surveillance. Internationally, they piloted cross border payments and settlement with central banks in places like Thailand and UAE. That’s the current concern.”
Copyright © 2023 IDG Communications, Inc.